Read about the latest advances in precision motion and automation
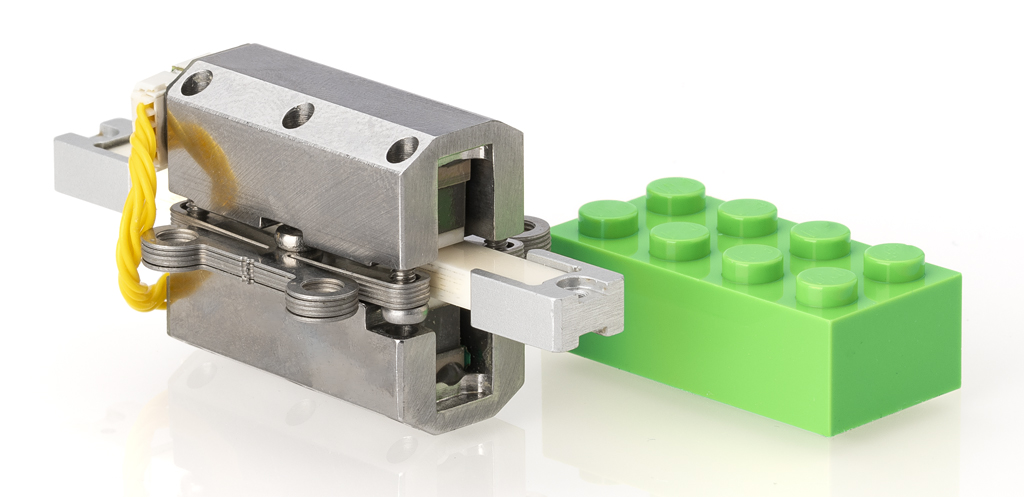
High precision PiezoMotors
The demand for higher accuracy in manufacturing is driving the development of precision machinery and measuring tools. Analytical instruments and manipulators in the medical sector are advancing and getting more exact. The semiconductor industry is continuously working with higher precision instruments to scale down devices on the silicon wafer. Wherever there’s a demand for the highest precision, there’s usually a need for a Piezo LEGS® motor.
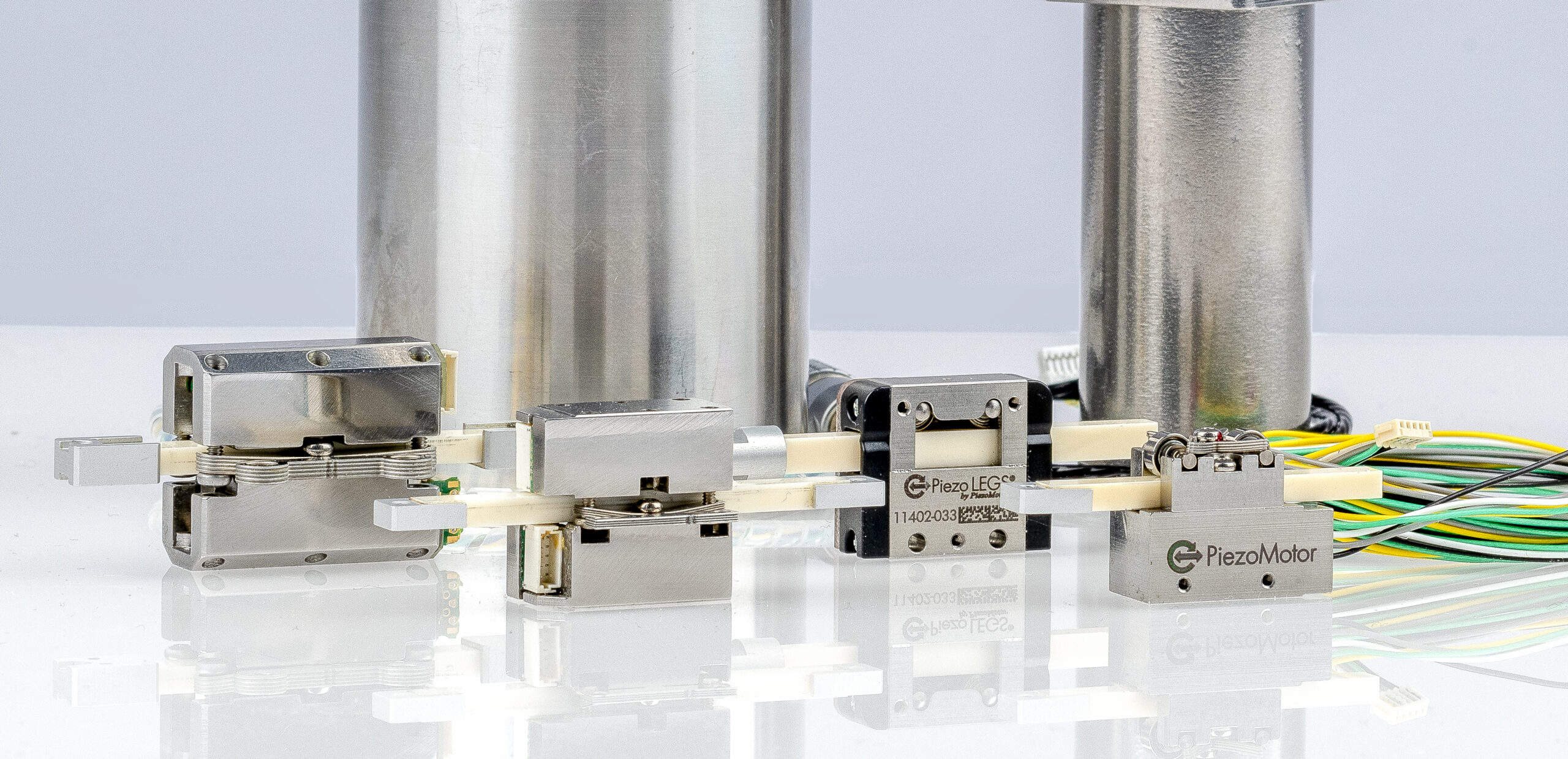

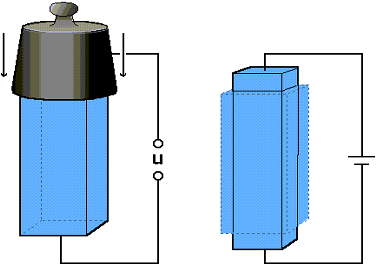
The Piezoelectric Effect and Its Application in Piezo Motor
The piezoelectric effect is a fascinating phenomenon where certain materials can generate an electric charge in response to mechanical stress. This unique property finds application in various fields, including the development of piezo motors, which are increasingly popular in precision electronic devices. This article delves into the piezoelectric effect, the inverse piezoelectric effect, and their critical roles in the functionality of piezo motors.
How to Select a high Precision Linear Stage
Navigating through the multitude of linear stage options available from various manufacturers, each offering extensive product lines but often limited guidance, can be a daunting task. However, selecting the right linear stage is essential for ensuring the success and efficiency of your application. To make a well-informed decision, you need to carefully evaluate several critical factors based on your specific research or operational requirements.

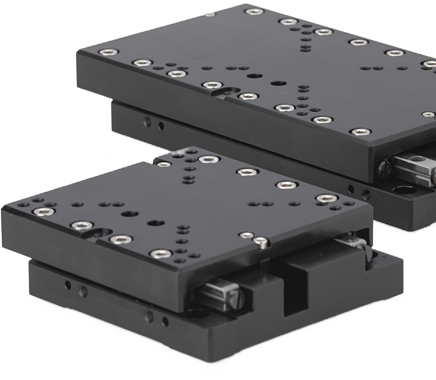
Understanding the Value of a High Precision Linear Stage
A linear stage excels in performing repetitive tasks or complex movement patterns with exceptional accuracy and reliability across various applications. This is particularly crucial in scenarios where even minor positioning errors can impact data integrity.
How to achieve high precision linear motion!
The most widely used technology for precision motion are the various variants of electric motors. Based on the power source, we differentiate between DC (direct current) and AC (alternating current) motors. Another main differentiation factor is the operating principle, which can be magnetism, electrostatics, or piezoelectricity.